Debt financing and equity financing are the two main types of financing companies use to raise capital for business needs. Naturally, you may be interested in understanding the difference between debt financing and equity financing, with the goal of determining the most suitable option for your specific situation.
Equity financing involves selling ownership stakes in the company to investors in exchange for capital. This can be in the form of common stock or preferred stock, which represents a share of ownership in the company. Equity financing allows companies to raise capital without incurring debt, but it also means that the company will have to share its profits with the investors. Additionally, equity financing typically involves giving up some control over the company, as the investors will have a say in the company's decisions.
Debt financing, on the other hand, involves borrowing money from lenders, such as banks, and repaying the loan with interest. This type of financing allows companies to raise capital without giving up ownership, but it does carry the obligation to repay the loan. Additionally, debt financing can involve higher costs in interest payments, which can impact a company's profitability.
In practice, most companies use a combination of debt and equity financing. The choice between debt and equity financing depends on the specific needs and circumstances of the company, including its financial position, growth prospects, and risk tolerance.
Equity Financing
Definition
Equity financing involves selling a portion of ownership in a company in exchange for capital. This can be done through the sale of stocks or other securities. Equity financing is a way for a company to raise capital without taking on debt. Instead of borrowing money and paying back the loan with interest, the company sells a portion of its ownership in exchange for capital.
An Initial Public Offering (IPO) is one way for a company to raise equity financing by selling shares of its stock to the public for the first time. This can be a complex and costly process, as the company must meet certain regulatory requirements and engage in extensive marketing efforts to attract investors. There are several other ways that companies can raise equity financing as well. For example, they can seek funding from angel investors, venture capital firms, or strategic investors who are interested in taking a stake in the company. Companies can also raise equity financing through private placement, where they sell shares to a small group of investors rather than going through a public offering.
One difference between debt financing and equity financing is that for equity financing, the company does not have to worry about repaying the capital that it receives. Instead of taking on debt and incurring interest charges, the company sells a portion of its ownership in exchange for capital. This can be a good option for companies that are looking to raise capital without taking on debt, or for companies that may have difficulty obtaining debt financing due to their risk profile or lack of collateral. While there is no obligation to repay the capital that is raised through equity financing, it is important to note that equity investors are taking on a certain level of risk when they invest in a company. If the company is successful, the equity investors may earn a good return on their investment. However, if the company is unsuccessful, the equity investors may lose some or all of their investment. This is one of the main differences between equity financing and debt financing, where the borrower is required to pay back the loan regardless of the company's performance.
However, there are also some disadvantages to equity financing. One of the main disadvantages is that the company is giving up a portion of ownership in exchange for capital, by selling equity in the company, the company's owners are giving up a portion of their control over the business and its decision-making processes. They will also be required to share the company's profits with the equity investors. Additionally, it can be challenging to buy out equity investors once they have become shareholders in the company. This may require the company to raise additional capital or sell assets to generate the funds needed to repurchase the equity. This process can be time-consuming and costly, and it may not always be feasible for the company.
It is important for companies to carefully consider the potential downsides of equity financing before deciding to pursue this type of funding. While equity financing can be a good option for some companies, it may not be the best choice for all businesses. Companies should carefully weigh the pros and cons of equity financing and consider all of their options before making a decision.
Types
Individual Investors
Individual investors, also known as retail investors or small investors, are individuals who invest in securities, such as stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and exchange-traded funds (ETFs). They may be friends, family members, or colleagues of business owners who are interested in investing in the business. Individual investors usually have less money to invest compared to institutional investors, so more of them may be needed to reach financing goals. While individual investors may not have relevant industry experience or business skills, they may still be able to contribute to a business in other ways. Additionally, many individual investors are looking for opportunities to support businesses that align with their values and beliefs, so they may be willing to invest in a business that is socially responsible or environmentally conscious.
It is important for business owners to carefully consider the potential benefits and drawbacks of accepting investments from individual investors. Business owners should be transparent about the risks and uncertainties of their business and be prepared to communicate clearly with individual investors about the potential returns on their investment. Business owners should also be aware of any legal or regulatory requirements for accepting investment from individual investors, such as securities laws and regulations.
Angel Investors
Angel investors are individual investors who provide capital to businesses. They are often wealthy individuals or groups who are looking for opportunities to invest in businesses that they believe have the potential to generate attractive returns. Angel investors can invest substantial amounts of money, and they are often more experienced and knowledgeable about business and investing compared to individual investors. Angel investors typically invest in the early stages of a business's development, such as during the seed or startup phase. They may also be willing to invest in businesses that are experiencing financial difficulties or are in need of additional capital to grow. In exchange for their investment, angel investors typically receive ownership stakes in the business, which allows them to share in the profits or losses of the company.
In addition to providing capital, angel investors can also contribute valuable insight, connections, and advice to businesses due to their industry experience. They may be able to provide guidance on key business decisions and help entrepreneurs navigate the challenges of starting and growing a business. However, it is important for business owners to carefully consider the terms of any investment from an angel investor, as well as the expectations and roles of the angel investor in the business. Business owners should also be aware of any legal or regulatory requirements for accepting investment from angel investors, such as securities laws and regulations.
Venture Capitalists
Venture capitalists are typically willing to take on more risk than traditional investors as they seek higher returns. They invest in businesses that have the potential to grow quickly and become very successful, but that also have a higher risk of failure. In exchange for their investment, venture capitalists usually receive a percentage of ownership in the company and may also have a say in the company's decision-making process.
Venture capital firms typically invest in more mature businesses that are looking to expand or restructure. In addition to providing capital, venture capitalists can also offer valuable resources and connections to help a company grow and succeed. They may have a network of industry experts and advisors who can provide guidance and support to the company. They may also have relationships with potential customers or partners that can help the company grow.
It's important to note that not all businesses are a good fit for venture capital funding. Venture capitalists are looking for companies with a clear path to profitability and a strong potential for growth. Companies that are not able to demonstrate these qualities may not be attractive to venture capitalists and may need to look for alternative sources of funding.
Initial Public Offerings
An initial public offering (IPO) is a process by which a privately held company sells shares of its stock to the public for the first time. IPOs are typically used by companies that have reached a certain level of growth and are looking to raise additional funds to finance further expansion. IPOs involve a significant amount of time, effort, and expense. The company must prepare and file a prospectus with the relevant regulatory authorities and go through the process of listing its stock on a public stock exchange. As a result, IPOs are typically only pursued by well-established companies that have a track record of success and a solid business plan.
Investors in an IPO typically expect to receive less control over the company than they would if they were venture capitalists or angel investors. However, they do receive ownership in the form of shares of stock, which may appreciate in value if the company is successful. It's important for investors to carefully consider the risks involved in investing in an IPO, as there is no guarantee that the company will be successful or that the stock will appreciate in value.
Crowdfunding
Crowdfunding is a way for companies, organizations, and individuals to raise money by soliciting small investments or donations from many people, typically through an online platform.
Crowdfunding can be a useful tool for companies and individuals to raise funds for various purposes, such as launching a new product or service, supporting a creative or artistic project, or raising money for a charitable cause. It can also be an attractive option for investors who are interested in supporting a company or project that aligns with their values or interests, and who may not have the financial resources to make a larger investment. However, it's important for investors to carefully consider the risks involved in crowdfunding, as there is no guarantee that the company or project will be successful or that the investor will see a return on their investment.
How it Works
Equity financing refers to the process of raising capital by selling ownership stakes in a company. There are several types of equity instruments that a company can use to raise capital, including common stock, preferred stock, convertible preferred stock, and equity units.
Common stock is the most basic form of equity and represents ownership in a company. It gives the holder the right to vote at shareholder meetings and to receive dividends if any are declared. Common stock is generally less expensive for the company to issue than preferred stock, but it also carries more risk for the investor as the holder of common stock is last in line to receive any payments in the event that the company is liquidated.
Preferred stock is a type of equity that has a higher claim on the company's assets and earnings than common stock. It may have a fixed or variable dividend, and it may also have a conversion feature that allows the holder to exchange the preferred stock for a certain number of common shares. Preferred stock is often used as a form of financing for early-stage companies because it offers the investor more protection than common stock.
Convertible preferred stock is a hybrid security that can be converted into common stock at the holder's discretion. It offers the investor the option to convert their preferred stock into common stock at a predetermined price, giving them the opportunity to participate in the potential appreciation of the company's stock. Convertible preferred stock is often used as a form of financing for early-stage companies because it allows the investor to convert their preferred stock into common stock at a later date, potentially giving them a higher return on their investment.
Equity units are securities that combine common stock and warrants into a single package. Warrants are options that give the holder the right to purchase additional common shares at a fixed price at a later date. Equity units are often used as a form of financing for later-stage companies because they can provide additional upside potential to the investor while also providing the company with additional capital.
Equity financing can be an important source of capital for startups and growing companies. It is important for a company to carefully consider its financing options and the terms of any equity instruments it issues in order to ensure that it is raising the right amount of capital at the right time and at terms that are favorable to the company and its shareholders.
Advantages
Alternative to Debt
Equity financing involves selling ownership stakes in a company in exchange for capital, rather than borrowing money and incurring debt. Equity financing is generally considered a lower risk option for the company because investors seek a return on investment rather than loan repayment. Furthermore, because the rewards can be substantial, investors are typically more interested in assisting you to succeed than lenders are.
Expertise in Business and Investment Professionals
Equity financing can be a valuable source of funding for businesses, especially for those that are in the early stages of development. Angel investors and venture capitalists are typically experienced business people who can provide valuable insights and guidance to the companies they invest in. They may also have connections to other potential investors or partners that can help the business grow and succeed.
Disadvantages
Profits Must Be Shared
When a company raises equity financing, it is essentially selling ownership stakes in the company to the investors. These investors become shareholders in the company. As shareholders, they are entitled to a share of the company's profits in the form of dividends, as well as a say in the company's decision-making process.
Ownership Is Diluted
When a business owner seeks funding from angel investors or venture capitalists, they will typically be required to give up a portion of ownership in the company in exchange for the investment. While obtaining funding from angel investors or venture capitalists can be a great way to help a business grow and succeed, it can also involve giving up a significant amount of control over the company. Business owners should be prepared to make decisions that may not align with their personal interests in order to protect the interests of the company and its shareholders.
More Costly Than Debt
Angel investors and venture capitalists typically expect a higher rate of return on their investment compared to what a lender might charge for a loan. This is because the investor is taking on a higher level of risk by investing in a company that may not yet be established or profitable. In exchange for this higher risk, the investor expects to receive a higher return on their investment.
Overall, equity financing can be a great way to access the resources and expertise you need to grow your business, but it's important to carefully weigh the advantages and disadvantages before making a decision.
Debt Financing
Definition
Debt financing involves borrowing money and agreeing to pay it back over time, typically with interest. The most common form of debt financing is a loan from a bank or other financial institution. Debt financing can be a good option for companies that need to raise capital quickly and do not want to give up equity in the company. Debt financing also comes with certain risks and obligations. The company is required to pay back the loan with interest, which can be a burden on the company's finances. Additionally, the lender may place certain restrictions on the company's activities in order to protect its investment. These restrictions may limit the company's flexibility and prevent it from taking advantage of opportunities outside of its core business.
It is important for companies to carefully consider their debt-to-equity ratio when deciding whether to pursue debt financing. A relatively low debt-to-equity ratio is generally seen as a positive sign by creditors, as it indicates that the company has a strong financial foundation and is able to manage its debt effectively. This can make it easier for the company to access additional debt financing in the future if needed.
Debt financing can offer a number of advantages for businesses; such as fixed payments which can make budgeting and forecasting easier for businesses; the lender has no control over the business; and the interest is tax-deductible
However, it's important to keep in mind that debt financing also comes with some risks and responsibilities. For example, businesses must make regular payments on the debt and may face financial penalties if they are unable to do so. In addition, taking on too much debt can strain a business's finances and potentially lead to financial difficulties.
How it Works
When a company needs to raise capital, it has a few options to consider. One option is to sell equity, which involves issuing shares of stock in the company to investors in exchange for capital. This allows the company to raise funds without incurring debt, but it also means that the company must give up a portion of ownership in the company to the investors.
Another option is to take on debt financing, which involves borrowing money from lenders such as banks, credit unions, or other financial institutions. Debt financing can take many forms, such as loans, bonds, or notes, and the company is required to pay back the principal amount of the loan, plus interest, at a later date. Debt financing allows a company to raise funds without giving up equity, but it also means that the company must pay back the loan, which can be a financial burden if the company is not generating sufficient profits.
Finally, a company can also consider using a hybrid of equity and debt financing, which involves both issuing shares of stock and taking on debt. This can be a good option for companies that want to raise capital without giving up too much equity, or for those that have limited access to debt financing. However, it's important for a company to carefully consider the advantages and disadvantages of each type of financing and to understand the potential impact on the company's ownership and financial obligations.
Advantages
Debt financing allows a business to leverage a small amount of capital to create growth
By borrowing money, a business can invest in new projects or expansion without having to use all of its capital.
Debt payments are generally tax-deductible
This can be a significant advantage, as it can reduce the overall cost of borrowing by reducing the amount of taxes a business has to pay.
A company retains all ownership control
Since the lender does not become an owner of the business, the company's management team can continue to make all the decisions regarding the business.
Often less costly than equity financing
When a company raises money through the sale of equity, it must share a portion of the ownership and profits with the new investors. This can be more expensive in the long run compared to paying back a loan with interest.
Disadvantages
Interest must be paid to lenders
When a business takes out a loan, it must pay back the principal amount plus an additional amount called interest. This can add to the overall cost of borrowing and strain the company's financial resources.
Payments on debt must be made regardless of business revenue
A business is required to make regular debt payments, regardless of whether it is generating enough revenue to cover the costs. This can be a problem for businesses that experience fluctuations in revenue or that are struggling financially.
Debt financing can be risky for businesses with inconsistent cash flow
If a business has unstable or uncertain cash flow, it may be difficult to make regular debt payments on time. This can lead to financial problems and potentially damage the business's credit rating.
Debt financing may limit a company's flexibility
When a business has a large amount of debt, it may have less flexibility to make investments or take on new projects. This can limit the company's growth and profitability.
Debt financing can lead to a loss of control
If a business takes on too much debt, it may be forced to give up control to the lenders in order to restructure the debt or avoid bankruptcy. This can be a significant drawback for business owners who value their independence and control over their company.
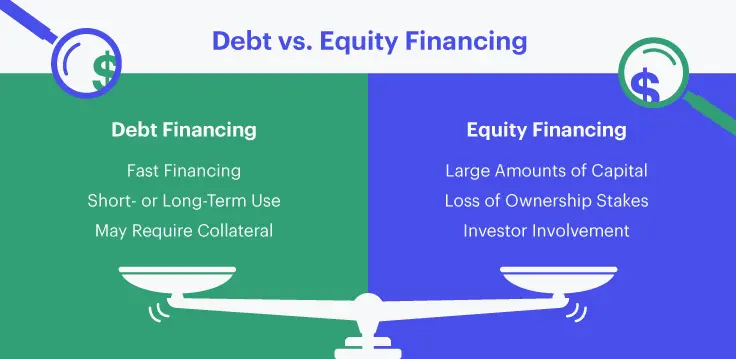
What Is The Difference Between Debt Financing and Equity Financing?
Key Differences
Debt financing and equity financing are two different types of financing methods that businesses can use to raise capital.
Debt financing involves borrowing money from lenders, such as banks, credit unions, or other financial institutions. The business is required to pay back the loan, including interest, over a predetermined period of time. Some common sources of debt financing include bank loans, corporate bonds, mortgages, overdrafts, credit cards, and asset-based financing.
Equity financing involves raising capital by selling ownership stakes in the company in the form of stocks or shares. This can be done through the sale of new shares to investors, or by issuing additional shares to existing shareholders. Some common equity financing sources include angel investors, venture capital firms, institutional investors, and retained earnings.
One key difference between debt financing and equity financing is that debt financing does not dilute ownership, while equity financing does. When a business takes on debt, it is required to pay back the loan and interest, but the ownership and control of the company remain with the existing owners. In contrast, when a business raises capital through the sale of equity, the new investors become owners of the company and have a say in its management and decision-making.
Another difference is that debt financing typically has a fixed repayment period and a fixed interest rate, while equity financing does not have a fixed repayment period and may not have a fixed interest rate. Instead, equity investors typically receive dividends when the company generates profits.
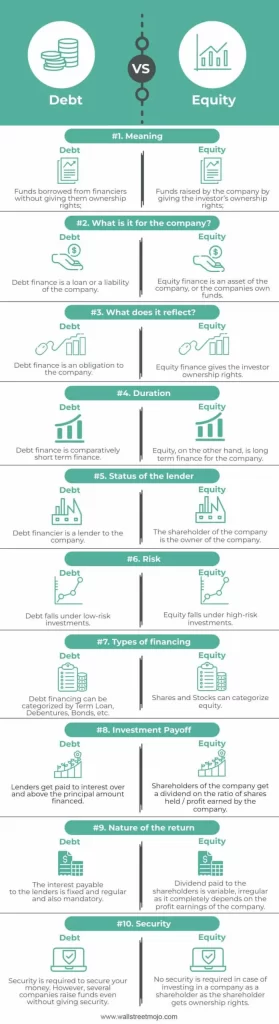
Comparative Table
| Base of Difference | Debt | Equity |
| Meaning | Funds borrowed from financiers without giving them ownership rights | Funds raised by the company by giving the investor ownership rights |
| What is it for the company | Debt finance is a loan or a liability of the company | Equity finance is an asset of the company or the company's own funds |
| What does it reflect | Debt finance is an obligation to the company | Equity finance gives the investor ownership rights |
| Duration | Debt finance is comparatively short-term finance | Equity is long-term finance for the company |
| Status of the lender | Debt financier is a lender to the company | The shareholder of the company is the owner of the company |
| Risk | Debt falls under low-risk investments | Equity falls under high-risk investments |
| Types of financing | Debt financing can be categorized by Term Loan, Debentures, Bonds, etc | Shares and Stocks can categorize as equity |
| Investment payoff | Lenders get paid interest over and above the principal amount financed | Shareholders of the company get a dividend on the ratio of shares held/ profit earned by the company |
| Nature of return | The interest payable to the lenders is fixed and regular and also mandatory | Dividend paid to the shareholders is variable, and irregular as it completely depends on the profit earnings of the company |
| Security | Security is required to secure your money. However, several companies raise funds even without giving security | No security is required in case of investing in a company as a shareholder as the shareholder gets ownership rights |
How to Choose Between Debt Financing and Equity Financing
Choosing between debt ad equity financing is a complex decision that depends on a variety of factors, including the type of business, the industry in which the business operates, and the company's financial situation. It's important to carefully weigh the advantage and disadvantages of each type of financing and to consider how they will impact the company's overall capital structure and financial health.
In general, debt financing involves borrowing money from lenders, such as banks or other financial institutions, and repaying the loan with interest over time. This can be a good option for businesses that have a solid credit history and can afford to make regular payments on their debt. However, borrowing money also carries the risk of default, which can have serious consequences for the business.
Equity financing, on the other hand, involves selling ownership stakes in the company to investors in exchange for capital. This can be a good option for businesses that don't have a solid credit history or that don't want to take on additional debt. However, selling equity also means giving up a portion of ownership and control in the company, which can be a difficult decision for some business owners.
Ultimately, the best option for a given business will depend on a variety of factors and will require careful analysis and consideration. It's important to do thorough research and consult with financial advisors and other experts to help make an informed decision.
Conclusion
In general, a company will choose debt financing over equity financing if it has the ability to pay back the borrowed funds and if it wants to retain ownership and control. However, if the company does not have strong cash flow or sufficient assets to secure debt financing, or if it is unable to meet the lender's requirements, it may need to turn to equity financing as an alternative.
References
Equity Financing vs Debt Financing