The Business Model Canvas (BMC) is a strategic management tool to quickly and easily define and communicate a business idea or concept. It is a set template of key components and activities that are associated with all types and industries of businesses. This model canvas helps you better understand your business model.
The right side of the BMC focuses on the customer (external), while, the left side of the canvas focuses on the business (internal). You can download and use a sample PDF template for a business canvas model below.
Why Is A Business Model Canvas Important
Why are business model canvases preferred more over a business plan. It is quite preferred amongst entrepreneurs and intrapreneurs for quite a lot of reasons:
- It strips the need for a multiple paged document, a business plan and helps keep everything concise and neat in a one-page document. Users of a business model canvas are up-to-date and have clarity on their core activities and focused on what is driving their business.
- Transparency. Your team will have a much easier time understanding your business model and be much more likely to buy into your vision when it’s laid out on a single page.
- Flexibility. It’s a lot easier to tweak the model and try things (from a planning perspective) with something that’s sitting on a single page.
However, this does not mean that you completely diminish the need for creating a business plan. Business plans are still highly important and may be needed for various proposals.
Key Components of A Business Model Canvas
The Business Model Canvas breaks your business model down into easily-understood segments: Key Partners, Key Activities, Key Resources, Value Propositions, Customer Relationships, Channels, Customer Segments, Cost Structure, and Revenue Streams. An example of what the business model canvas looks like is displayed below. The contents for each component is discussed below.
Key Partners
Key Partners are a list of other external companies/suppliers/parties you may need to achieve your key activities and deliver value to the customer. This answers the question that ‘if my business cannot achieve the value proposition alone, who else do I need to rely on to do it?’ 'Who are the external supporters for my business?'.
An example of this is ‘if I sell groceries to customers, I may need a local baker to supply fresh bread to my store’. They are a key partner to achieve the value my business promises to the customer.
Key Activities
The Key Activities of your business/product are the actions that your business undertakes to achieve the value proposition for your customers. In other words, these can also be processes that must be completed in order for you to serve your customers. There are a few questions to be considered while you are planning out your business's key activities.
- What activities does the business undertake in achieving the value proposition for the customer?
- What is the resource used?
- Time?
- Expertise?
- Distribution of the product?
- Technical development?
- Strategy?
- Offer resources (human/physical)?
- What actions does it take you and/or your staff to achieve value exchange?
These might include sales calls, workshop delivery, meal preparation or writing reports. In particular, these are the activities that your business is able to do particularly well.
Key Resources
These are the resources that your business will need to fulfil your key activities. A list of these will generally include the following: Office space, computers, people (staff), internet connection, kitchen equipment. These resources are entirely dependent on the type of business you are running and/or the industry you are based in. A few types of key resources are:
- Physical Resources. Physical assets are tangible resources that a company uses to create its value proposition. These could include equipment, inventory, buildings, manufacturing plants and distribution networks that enable the business to function.
- Human Resources. Employees are often the most important and yet the most easily overlooked assets of an organization. Specifically for companies in the service industries or require a great deal of creativity and an extensive knowledge pool, human resources such as customer service representatives, software engineers or scientists are pivotal i.e. drivers and transporters for FedEx.
- Intellectual Resources. These are non-physical, intangible resources like brand, patents, IP, copyrights, and even partnerships. Customer lists, customer knowledge, and even your own people represent a form of intellectual resource. Intellectual resources take a great deal of time and expenditure to develop.
- Financial Resources. The financial resource includes cash, lines of credit and the ability to have stock option plans for employees. All businesses have key resources in finance, but some will have stronger financial resources than others, such as banks that are based entirely on the availability of this key resource.
Value Propositions
This section of the business model canvas is the most fundamental. It is the concept of the exchange of value between your business and your customer/clients. For this section, you need to understand what the customer wants so they will be willing to happily pay for the value proposition that they are receiving via your product/service.
A few questions to ask yourself before you draw up your value proposition.
- What is the problem I am solving?
- Why would someone want to have this problem solved?
- What is the underlying motivator for this problem?
There are multiple areas where a business can add value, build its value proposition. A few to mention are the newness of the product, high performance in comparison to the price, ability to customize, design and features of the product/service, brand and the status that comes with the product purchase, the amount of risk reduction is offered.
Customer Relationships
Customer relationships are the definition of how a business interacts with its customers; how do you acquire customers, how do you retain them and how do you grow them? Customer relationships are built and created through customer acquisition, customer retention and boosting sales for repeat purchases.
Your customers may have certain expectations about the kinds of relationships you should establish with them. It can be helpful to think about what these might be and how best to implement them. It depends on the type of experience that they are expecting to receive from you. There are various types of customer service as well, some of the most commonly found are as below:
-
Personal Assistance: This type of customer relationship is concerned with human communication. This could be via phone, email, face-to-face or any other means of communication.
-
Dedicated Personal Assistance: This relationship is more personal as it is individually tailored. It includes assigning a customer representative to a specific customer so they are consistently engaging with the same person. This provides familiarity, builds trust and allows the customer representative to really get to know and understand that particular client. Additionally, this personalised service can foster deep and meaningful relationships with important customers over a prolonged period.
- Self-service: In contrast, this relationship entails no direct relationship between a business and its clients. Customers are entirely self-sufficient so there is no need to establish any human interaction with them.
Channels
This building block outlines how you communicate with customers to deliver your Value Proposition. This could be done through either offline or online channels such as face-to-face or via social media. Channels are the avenues through which your customer comes into contact with your business and becomes part of your sales cycle.
This is generally covered under the marketing plan for your business. However, there are a few questions to ask yourself before panning out the channels for your business:
- How are we going to tell our customer segment about our value proposition?
- Where are our customers?
- Are they on social media?
- Are they driving their car and listening to the radio?
Some examples of channels that businesses will use as social media, targeting blogs, electronic mail (email marketing), trade shows, public speaking, networking, offline advertising (billboards, TV, radio). There are plenty more and these are only to name a few.
Amongst all others, channels are one of the most vital blocks because understanding how to reach out to your customers is perhaps one of the most important.
Customer Segments
Customer segmenting is the practice of dividing a customer base into groups of individuals that are similar in specific ways, such as age, gender, interests and spending habits. This is done because not all customers belonging to different backgrounds will have the same product/service needs. Yet again there are a few questions that you will need to ask yourself before outlining your customer segment:
- Who is the target market for your product/service and how are you going to target them?
- What are the characteristics of the people who are looking for my value proposition?
- Does my value proposition appeal to men/women or both?
- Does it appeal to young adults aged 20 to 30 or teenagers? What is the age of customers that I am targeting?
Another thing to gauge and understand is your market size, and how many people there are in the Customer Segment. This will help you understand your market from a micro and macro perspective.
Cost Structure
This block will basically tell you your cost centres and what is the cost for running your business. You can identify the cost areas by answering some of the following questions.
- How much does it cost to achieve my businesses key activities?
- What is the cost of my key resources and key partnerships?
- How much does it cost to achieve the value proposition for my customers/users?
- Are there additional costs for running a business?
- What is the cost of my business?
- It is important also to place a monetary value on your time as a cost.
- How much would it cost you to hire?
- What is the opportunity cost of running your business?
Revenue Streams
Revenue Streams are defined as the way by which your business converts your Value Proposition or solution to the customer’s problem into financial gain. It is basically what is the source of income for your business and how your business makes money. Every business will have its own revenue model, a few to name are pay per product (pay per view), a fee for service, subscription, dividends, freemiums and much more.
Using all of the nine components above, below is a short video on how to compile those components and create a business model canvas for your own business.
Business Model Canvas and Organisational Efficiency
Innovation is disruptive. But, not every business is prepared for disruption. Without a plan, it is next to impossible. For an organisation to innovate, it has to have a fine-tuned strategy that guides it towards a viable future business model. Using a tool like the Business Model Canvas can serve to unite your company under a clear visualisation of where your organisation sits today and where it can be tomorrow (and how it will get there).
| Grouping | Business Model Component |
| Product | Value Proposition - exchange of value via products and services to customers |
| Customer Interface |
Customer Relationships - how your business interacts with its customers Channels - what are the channels of distribution that your business uses to get its products and services to potential customers Customer Segment - dividing the customer base into segments based on their demographics |
| Infrastructure Management |
Key Activities - the activities that your business undertakes to deliver value to its customers Key Resources - resources required by businesses to undertake their key activities Key Partners - providers and suppliers of the business that helps the business achieve their processes |
| Financial Aspects |
Cost Structure - the costs of running your business Revenue Stream - streams how your business receives revenue from selling value proposition |
The Business Model Canvas moves innovation out of the 'in theory stage and into the planning stage. For example, what your strongest revenue streams are and how they can complement each other. Or, more closely examine your value propositions and discover better ways to position your product or service to customers. Use customer segments to find out exactly who you're talking to and how to approach them more effectively.
Business Model Canvas Examples
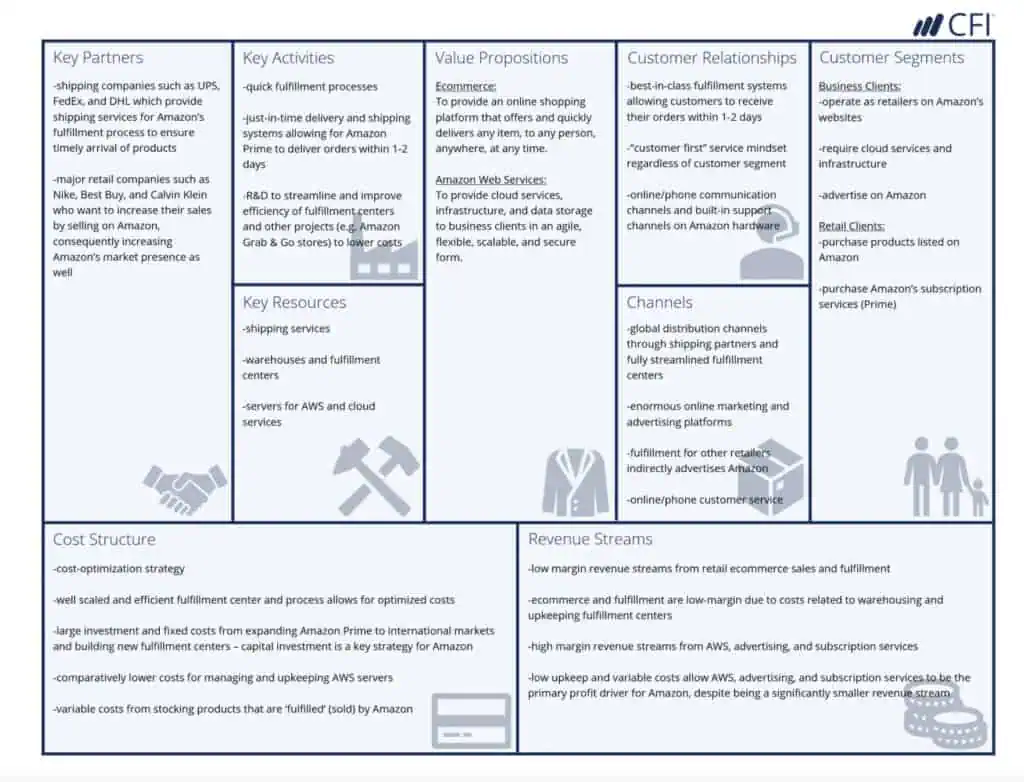
A prepared example of a business model canvas taken from the Corporate Finance Institute (CFI), based on the e-commerce giant, Amazon.
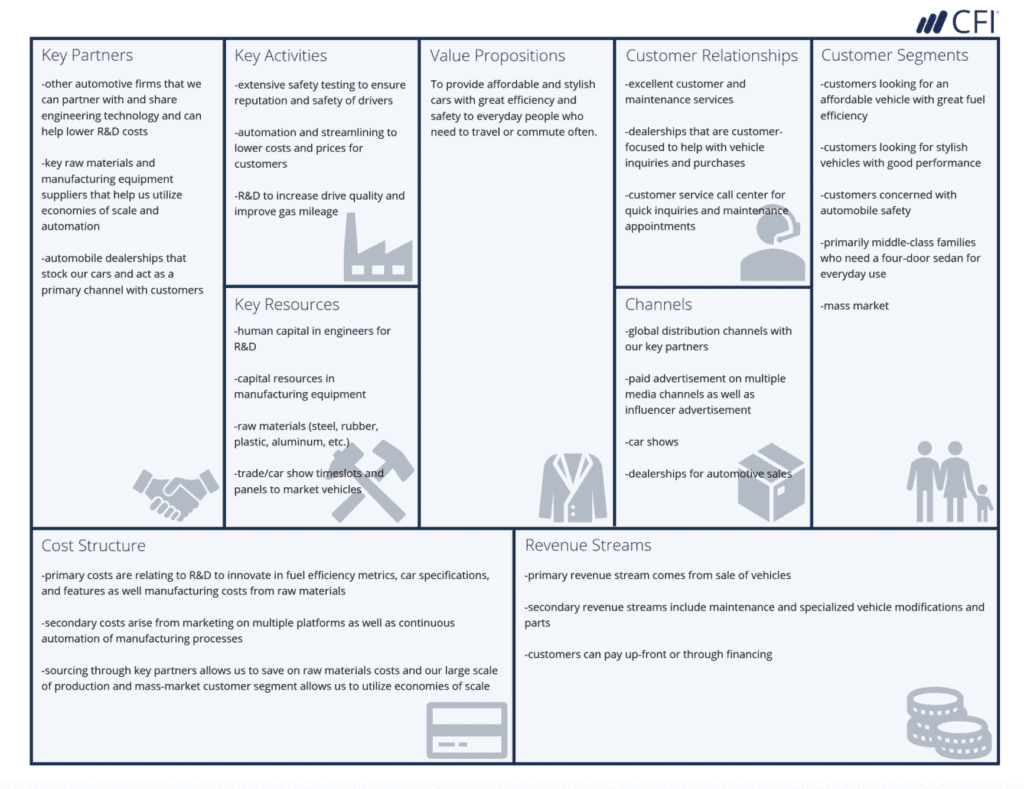
Another example provided by CFI is regarding the automobile industry. This is applicable to companies like Audi, Toyota, Honda and/or any in similar industries.
To Conclude
In conclusion, it is important to stay ahead of the curve and develop a business model canvas instead of a business plan. By digging into these nine elements of your company, you can recognize and act on areas that can be improved. It also reveals clear paths on which to build your organizational strategy.
The nine key elements of a business model canvas help you document an in-depth, succinct and clear definition of your business. By focusing on aspects apart from product development, it gives you the competitive edge to launch a profitable startup.
References
Benefits of Using A Business Model Canvas Over A Business Plan






